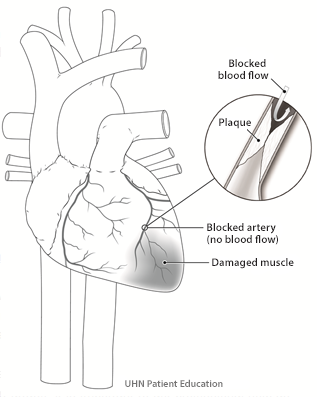
Heart attack in the front part of the heart muscle.
When there is a complete blockage of the coronary artery, a heart attack or “infarct” may occur.
During a heart attack part of the heart does not receive any blood or oxygen. The lack of blood and oxygen can damage that part of the heart muscle. When there is damage to the heart muscle, the heart’s ability to pump blood may be affected.
During a heart attack you may feel some or all of the following symptoms:
- chest discomfort, squeezing, pressure, burning, or heaviness
- discomfort in the neck, jaw, back, arms, or shoulders
- shortness of breath
- sweating
- nausea
- light-headedness
It is important to know that different people have different symptoms. Men and women can also experience different symptoms.
Although these are the most common symptoms felt during a heart attack, some people may experience a combination of them while others may not feel any of them. The symptoms can be similar to angina symptoms but more intense.
Many people deny that they feel symptoms. If you feel any of these symptoms and they are not relieved by rest or Nitroglycerine, call 9-1-1 or your local emergency department for help.
If you are having a heart attack, it is important to get professional help as quickly as possible to try to reduce the amount of damage to your heart.
See what happens when you have a heart attack (opens in new window) »